Running Classic Monte Carlo
As a simple example for classic Monte Carlo we consider obtaining a phase transition in 2D Ising model.
First step we need to import required packages
import pyalps
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pyalps.plotPrepare the input parameters
parms = []
for l in [4,8,16]:
for t in [5.0,4.5,4.0,3.5,3.0,2.9,2.8,2.7]:
parms.append(
{
'LATTICE' : "square lattice",
'T' : t,
'J' : 1 ,
'THERMALIZATION' : 1000,
'SWEEPS' : 400000,
'UPDATE' : "cluster",
'MODEL' : "Ising",
'L' : l
}
)
for t in [2.6, 2.5, 2.4, 2.3, 2.2, 2.1, 2.0, 1.9, 1.8, 1.7, 1.6, 1.5, 1.2]:
parms.append(
{
'LATTICE' : "square lattice",
'T' : t,
'J' : 1,
'THERMALIZATION' : 1000,
'SWEEPS' : 40000,
'UPDATE' : "cluster",
'MODEL' : "Ising",
'L' : l
}
)Here we consider lattices of sizes $4\times 4$, $8\times 8$, $16\times 16$, for different temperatures.
After that we write the input into ALPS specific format and run spin Monte Carlo simulation (spinmc):
#write the input file and run the simulation
input_file = pyalps.writeInputFiles('parm7a',parms)
pyalps.runApplication('spinmc',input_file,Tmin=5)After the simulation is finished we can evaluate and plot the results.
pyalps.evaluateSpinMC(pyalps.getResultFiles(prefix='parm7a'))
#load the susceptibility and collect it as function of temperature T
data = pyalps.loadMeasurements(pyalps.getResultFiles(prefix='parm7a'),['|Magnetization|'])
magnetization_abs = pyalps.collectXY(data,x='T',y='|Magnetization|',foreach=['L'])
#make plots
plt.figure()
pyalps.plot.plot(magnetization_abs)
plt.xlabel('Temperature $T$')
plt.ylabel('Magnetization $|m|$')
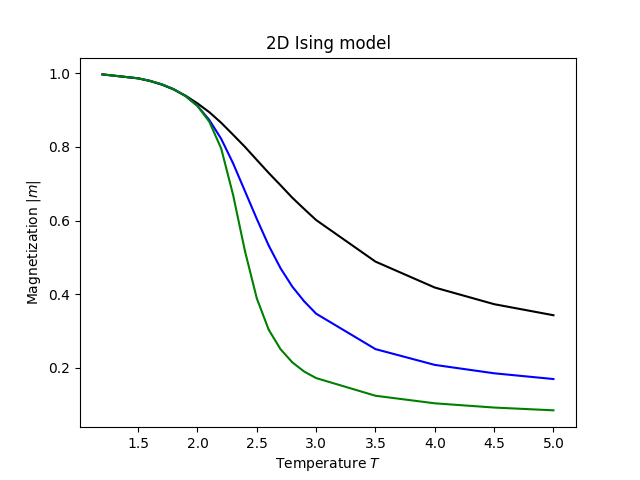
plt.title('2D Ising model')
plt.show()After that we should obtain the following figure for magnetization in 2D Ising model